
Law of superposition states that the younger rocks are deposited over the older one. Arrange the relative ages of the features in order from youngest to oldest of outcrop C? Thinnest rock. Distinctive rock layers, such as the Coconino Sandstone, are matched across the. Is the intrusion of igneous rock younger or older? Second oldest rock: This rock layer is just above the oldest. First week only $4.99! Lopolith,Batholith, Laccolith, Stock. Next, arrange your rocks in a stack, like the one below, and number the layers from 1 to 6 (with 1 being the oldest and 6 being the youngest). This is an example of the Principle of _. Drag the rock layers from the tools panel to the diagram and arrange them from oldest to youngest. Drag and drop the text labels onto the diagram. Use this interactive to work out the relative ages of some rock layers from youngest to oldest. What environmental condition takes place in rock layer no.3? X M Fig. Which shows the correct order from oldest to youngest layers? What do you mean by Soil layers? The youngest layer is the layer 3 because it corresponds to an intrusion that brakes through others and appears across. Start at the bottom (oldest) and list to the youngest event. Based on this, layer C is oldest, followed by B and A. a stack of papers, and trash in a trash can to show that the things or layers at the bottom are the oldest, or were placed there first, while the things or layers. Repeat this process until you get four marks. Second oldest rock: This rock layer is just above the oldest. the inhabitants of the area likely deposited the trash by throwing it in from the top, eventually filling the pits. Reconstruct the Geologic History of the area based on the given cross section diagram, from the oldest event to the youngest. The many horizontal layers of sedimentary rock illustrate the principle of original horizontality (Figure below). Solution for Arrange the layers from oldest to youngest in the picture. Answer: The youngest fossil is the Foraminniferan. The metamorphic schist (#16) is the oldest rock formation and the cross-cutting granite intrusion (#17) is younger. (fault, erosion) layer 1 layer 2 layer 3 layer 4 Question: Arrange the following in their correct order, from oldest at the bottom (4) to youngest at the top (1). Did the movement through the fault (N) occur after the before or deposition of layer (3)? First week only $4.99! The statement that the oldest layer will be at the bottom in an undisturbed sequence of rock layers is called the Principle of. Second, we observe that rock layer H (which is an igneous intrusion) cuts into rock layers B-F. Indicate the important events and environmental changes that occurred up until the last deposited layer or the last known event. For each of the following pairs of rock layers identify the relative dating principle that you used to determine which bed was older and which was younger. Don't let the patterns trip you up, they represent the type of rock the layer.
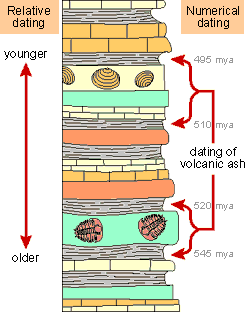
Relative age of trash layers - Because of the shape of the pits the oldest layers of trash occur below younger layers i.e. What rock layer is common in each rock column? Second oldest rock.
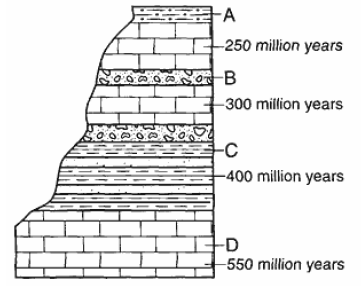

R4 DN arrange the layers of rock oldest.
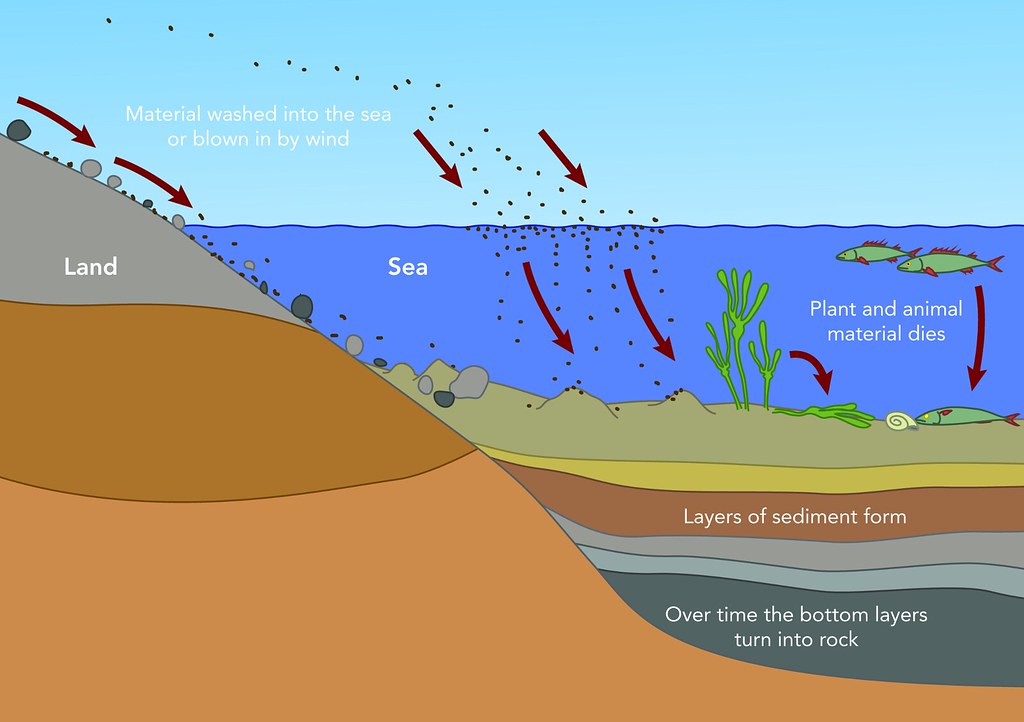
Science Earth Sciences Earth Sciences questions and answers 5 points Arrange the layers from oldest to youngest (1 - oldest and 5 - youngest layer). Arrange them from oldest to youngest with the oldest layer on the bottom and the youngest on top. Soil layers may be defined as the parallel arrangement of different layers on the basis of their physical, chemical, and biological characteristics. TOOLS youngest Breccia Conglomerate Age Dolostone Shale oldest Interpretation Questions: 1. These are erosion surfaces, hiatuses, or gaps in time, such as the erosion surface shown by the red arrow. What kind of each? The youngest rock layers are at the top and the oldest are at the bottom, which is described by the law of superposition. Pages 23 This preview shows page 19 - 23 out of 23 pages.preview shows page 19 - 23 out of 23 pages. Press the? This layer formed on top of earlier rocks. The rock strata are in order from oldest, at the bottom, to youngest, at the top, and all of the layers have a name that represents the time period in which they were formed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
